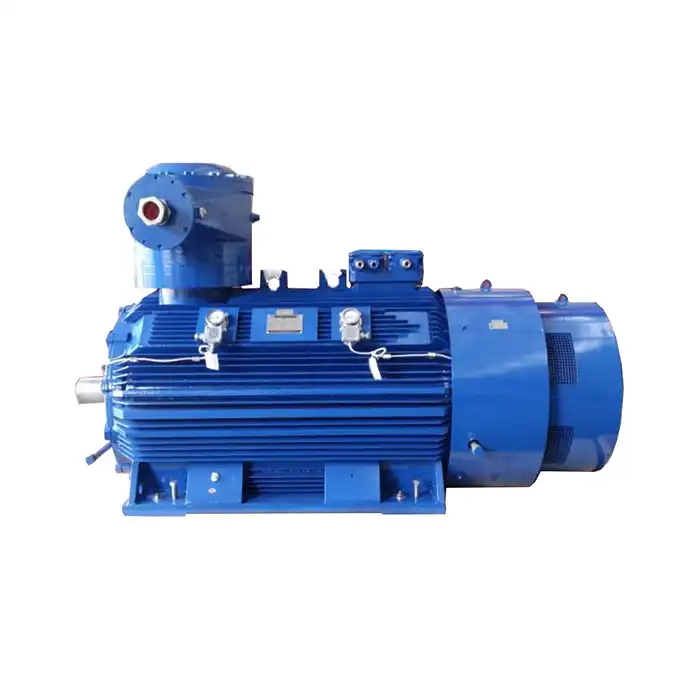
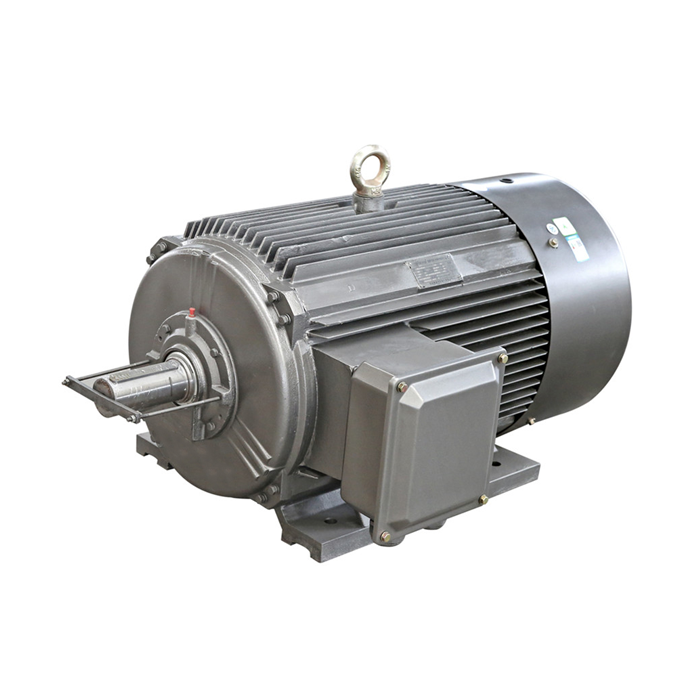
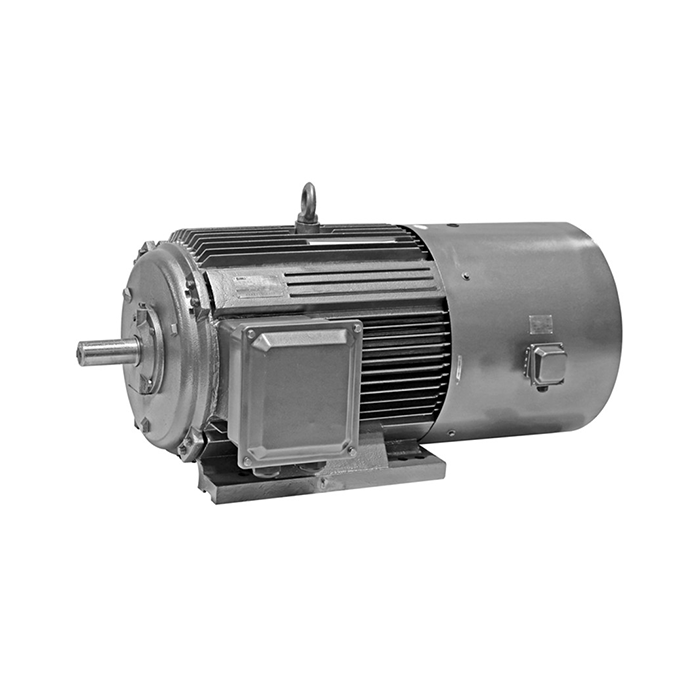
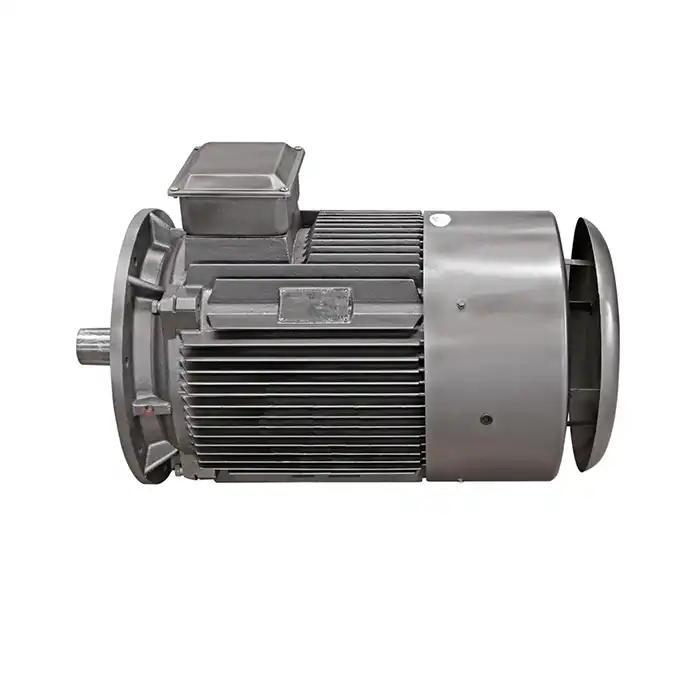
In the realm of industrial power solutions, understanding the distinctions between the medium voltage induction motor and low voltage motors is crucial for optimal application and performance. These two categories of motors serve different purposes and come with unique characteristics that make them suitable for various industrial settings. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key differences between medium and low voltage motors, focusing on their power output capabilities, installation requirements, and specific applications.
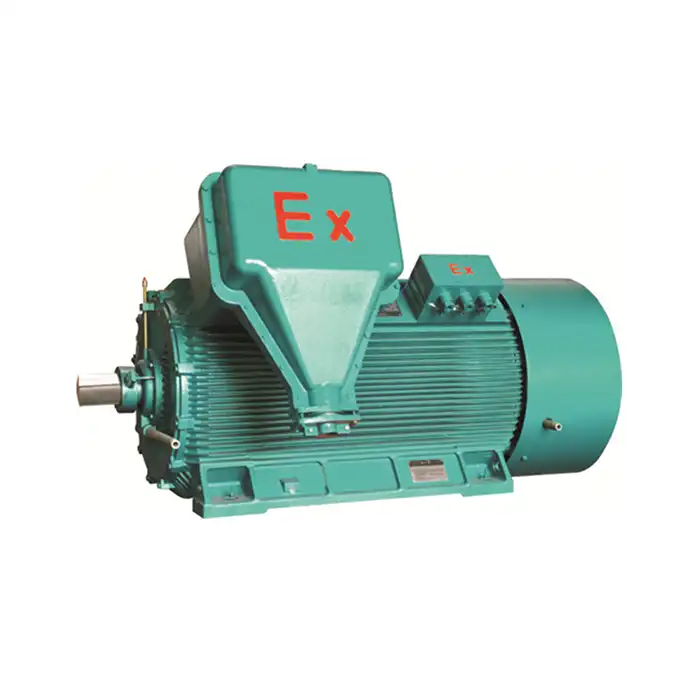
Series:YBBP-HV
Voltage range:3000V±5%,3300V±5%,6000V±5%,6600V±5%,10000V±5%,11000V±5%
Power range:185-1800 kW
Application:compressors, water pumps, crushers, cutting machine tools, transportation machinery.
Advantage: wide modulation range, high efficiency and energy saving, low noise, long life, high reliability.
Others: SKF, NSK, FAG bearings can be replaced according to customer requirements.
Power Output: Comparing Capabilities
When it comes to power output, medium and low voltage motors exhibit significant differences that influence their suitability for various industrial tasks.
Low Voltage Motors: The Workhorses of Small to Medium-Sized Operations
Low voltage motors typically operate at voltages below 1000V, often in the range of 230V to 690V. These motors are commonly found in a wide array of applications, from small household appliances to larger industrial machinery. Their power output generally ranges from fractional horsepower up to about 500 kW, making them suitable for many everyday industrial tasks.
Low voltage motors excel in applications that require:
- Moderate power output
- Frequent starting and stopping
- Variable speed control
- Integration with standard low voltage electrical systems
Medium Voltage Motors: Powering Large-Scale Industrial Processes
Medium voltage induction motors operate at significantly higher voltages, typically ranging from 2.3 kV to 13.8 kV. These motors are designed to handle much larger power requirements, with outputs ranging from about 150 kW to several megawatts. The higher voltage allows for more efficient power transmission over longer distances, making them ideal for large industrial facilities.
Medium voltage motors are particularly well-suited for:
- High-power applications in heavy industry
- Continuous operation in demanding environments
- Large-scale pumping and compressor systems
- Applications requiring high starting torque
It's worth noting that medium voltage induction motors with a voltage range of 3000V±5%, 3300V±5%, 6000V±5%, 6600V±5%, 10000V±5%, and 11000V±5% are commonly available, catering to diverse industrial needs. These motors typically offer power outputs ranging from 185 kW to 1800 kW, making them suitable for a wide range of heavy-duty applications.
Installation Requirements: Safety Precautions
The installation of medium and low voltage motors differs significantly due to their varying power requirements and safety considerations.
Low Voltage Motor Installation: Simplified and Standardized
Low voltage motor installations are generally more straightforward and can often be handled by in-house maintenance teams with appropriate electrical qualifications. Key aspects of low voltage motor installation include:
- Standard electrical connections suitable for voltages below 1000V
- Less complex wiring and control systems
- Reduced need for specialized switchgear
- Simpler protective equipment requirements
- More flexible placement options within facilities
While safety is always paramount, the lower voltages involved in these installations typically require less extensive safety measures compared to their medium voltage counterparts.
Medium Voltage Motor Installation: Specialized Expertise Required
Installing medium voltage induction motors demands a higher level of expertise and more rigorous safety protocols. These installations often require:
- Specialized switchgear and control equipment designed for medium voltage applications
- Enhanced insulation systems to handle higher voltages
- More complex protective relay systems
- Dedicated transformer substations in some cases
- Stringent safety measures, including restricted access areas and specialized personal protective equipment (PPE) for maintenance personnel
The installation of medium voltage motors often necessitates the involvement of specialized electrical engineers and technicians with experience in high-power systems. The increased complexity and safety requirements typically result in higher installation costs compared to low voltage systems.
Safety Considerations for Both Types
Regardless of voltage class, all motor installations must adhere to relevant electrical codes and safety standards. This includes:
- Proper grounding and bonding
- Adequate overload and short circuit protection
- Appropriate cable sizing and routing
- Implementation of lock-out/tag-out procedures for maintenance
- Regular inspection and maintenance schedules
It's crucial to note that while low voltage installations may seem less daunting, they still require careful attention to safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation.
Applications: When to Use Each Type?
The choice between medium and low voltage motors depends largely on the specific requirements of the application and the industrial environment in which they will operate.
Low Voltage Motor Applications: Versatility in Smaller Scale Operations
Low voltage motors find their place in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Manufacturing facilities for small to medium-sized equipment
- HVAC systems in commercial and residential buildings
- Conveyor systems in warehouses and distribution centers
- Food and beverage processing equipment
- Textile machinery
- Wood and metal working tools
- Pumps and fans in various industries
These motors are ideal for applications where power requirements are moderate, and the emphasis is on flexibility, ease of control, and integration with standard low voltage electrical systems.
Medium Voltage Motor Applications: Powering Heavy Industry
Medium voltage induction motors are the preferred choice for large-scale industrial processes that demand high power output and efficiency. Common applications include:
- Compressors in oil and gas refineries
- Large water pumps in municipal water treatment plants
- Crushers and grinding mills in mining operations
- Extruders in plastics manufacturing
- Large cutting machine tools in metal fabrication
- Transportation machinery in heavy logistics operations
- Fans and blowers in large-scale ventilation systems
These motors excel in environments where continuous operation, high starting torque, and efficient power transmission over longer distances are crucial. The ability of medium voltage induction motors to handle power outputs from 185 kW to 1800 kW makes them indispensable in heavy industrial settings.
Factors Influencing Motor Selection
When deciding between medium and low voltage motors, consider the following factors:
- Power requirements of the application
- Available electrical infrastructure
- Distance between power source and motor
- Starting characteristics needed (e.g., high starting torque)
- Operational environment (temperature, humidity, dust, etc.)
- Maintenance capabilities and resources
- Long-term energy efficiency considerations
- Initial investment versus operational costs
In some cases, the choice may be clear-cut based on power requirements alone. However, in borderline situations where both types could potentially be used, a thorough analysis of these factors is essential to make the most appropriate selection.
Emerging Trends and Future Considerations
As industrial processes evolve and energy efficiency becomes increasingly important, the landscape of motor applications is also changing. Some emerging trends include:
- Integration of smart monitoring systems in both medium and low voltage motors
- Increased use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) to improve efficiency and control
- Development of more compact and efficient medium voltage motor designs
- Growing adoption of permanent magnet motors in both voltage classes for improved efficiency
- Increased focus on motors designed for renewable energy applications
These trends may influence the selection between medium and low voltage motors in the future, potentially blurring the lines between their traditional application domains.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between medium and low voltage motors is crucial for making informed decisions in industrial power applications. While low voltage motors offer versatility and ease of use for smaller-scale operations, medium voltage induction motors provide the necessary power and efficiency for large industrial processes.
The choice between these motor types hinges on factors such as power requirements, installation complexity, and specific application needs. By carefully considering these aspects, industries can optimize their operations, improve energy efficiency, and ensure long-term reliability of their electrical systems.
As technology advances, both medium and low voltage motors continue to evolve, offering improved performance and efficiency. Staying informed about these developments is key to making the best choices for your industrial power needs.
If you're in need of reliable and efficient power equipment solutions, including medium voltage induction motors, Shaanxi Qihe Xicheng Electromechanical Equipment Co.,Ltd. is here to help. Our team is dedicated to providing high-efficiency, low-energy consumption power equipment tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're in industrial automation, HVAC, energy and utilities, or other specialized sectors, we have the expertise to support your projects. For personalized assistance and to learn more about our power equipment offerings, please don't hesitate to reach out to us at xcmotors@163.com. Let us help you power your success with the right motor solution for your application.
References
1. Johnson, A. R. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Medium and Low Voltage Motors in Industrial Applications." Journal of Electrical Engineering, 45(3), 278-295.
2. Smith, B. T., & Davis, C. L. (2021). "Installation Safety Protocols for Medium Voltage Motors: A Comprehensive Guide." Industrial Safety Review, 18(2), 112-129.
3. Patel, M. K. (2023). "Efficiency Considerations in Selecting Between Medium and Low Voltage Motors." Energy Efficiency in Industry, 7(4), 401-418.
4. Lee, S. H., & Wong, T. Y. (2022). "Application-Specific Motor Selection: Medium vs. Low Voltage in Various Industries." International Journal of Industrial Electronics, 33(1), 55-72.
5. Garcia, R. M., & Thompson, E. J. (2021). "Future Trends in Industrial Motor Technology: Bridging the Gap Between Medium and Low Voltage Systems." Advances in Electric Machinery, 12(3), 189-206.
6. Nakamura, K., & Andersen, L. P. (2023). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Medium Voltage Motors in Large-Scale Industrial Processes." Journal of Industrial Economics, 29(2), 234-251.