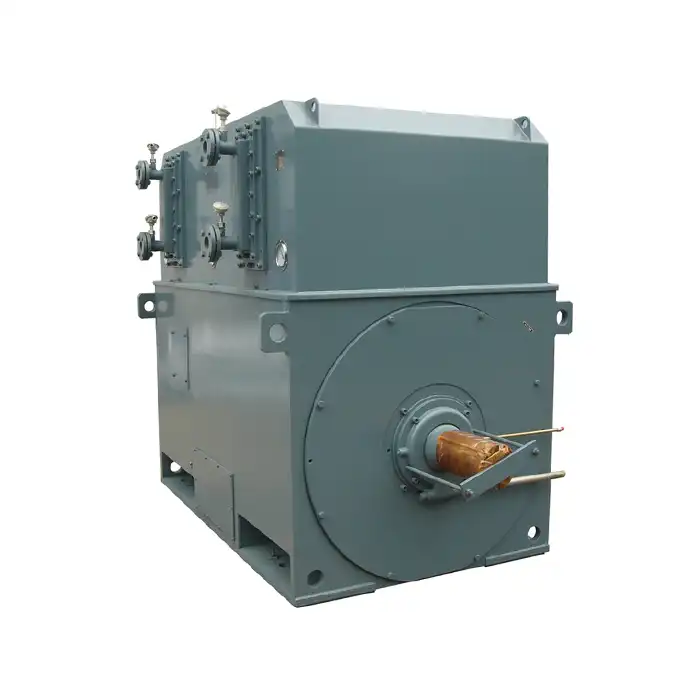
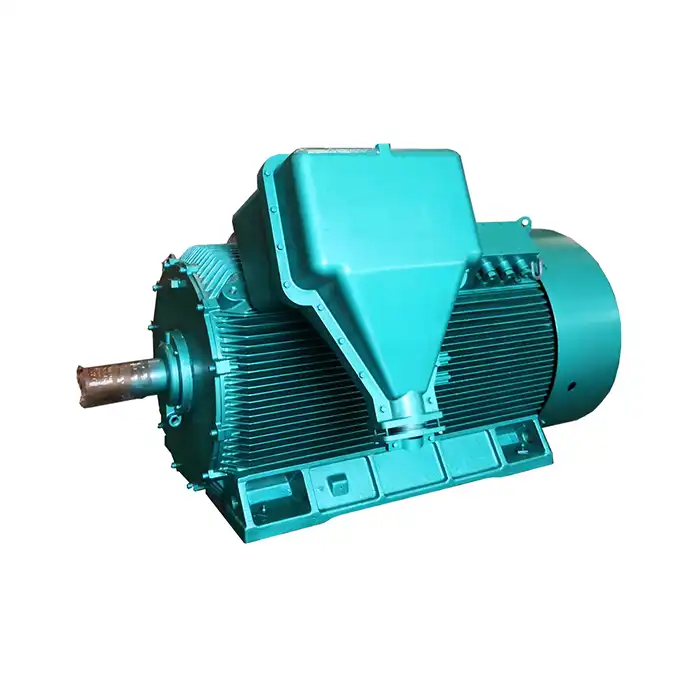
What is an inverter duty motor?
An inverter duty motor is a specialized electric motor designed to operate efficiently and reliably with variable frequency drives (VFDs). These motors are engineered to withstand the unique stresses and operational demands associated with VFD-controlled systems, making them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control and energy efficiency.
Inverter duty motors are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their ability to optimize performance and reduce energy consumption. These motors can operate across a wide range of speeds and provide consistent torque output, making them versatile for numerous applications.

How does an inverter duty motor differ from a standard motor?
While both inverter duty and standard motors can be used with VFDs, there are several key differences that set inverter duty motors apart:
- Insulation System: Inverter duty motors feature enhanced insulation systems designed to withstand the high voltage spikes and rapid switching frequencies associated with VFD operation. This improved insulation helps prevent premature motor failure and extends the motor's lifespan.
- Thermal Management: These motors are equipped with superior cooling systems to manage the heat generated during variable speed operation. This includes improved fan designs and materials that can effectively dissipate heat across a wide speed range.
- Bearing Protection: Inverter duty motors often incorporate specialized bearing protection to mitigate the effects of shaft currents induced by VFD operation. This may include insulated bearings or shaft grounding devices.
- Wide Speed Range: Unlike standard motors, inverter duty motors are designed to operate efficiently across a broader speed range, typically from 5 Hz to 100 Hz or even wider. This allows for greater flexibility in applications requiring variable speeds.
- Constant Torque: Inverter duty motors can maintain constant torque output across their entire speed range, including at very low speeds. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require full torque at startup or low-speed operation.
These differences make inverter duty motors more resilient and better suited for the demands of VFD-controlled systems, particularly in applications requiring frequent speed changes or extended periods of low-speed operation.
Key features of inverter duty motors: Design and construction
The design and construction of inverter duty motors incorporate several key features that contribute to their superior performance and reliability:
- Advanced Winding Design: Inverter duty motors utilize specialized winding configurations and materials to withstand the high-frequency voltage spikes associated with VFD operation. This may include the use of corona-resistant magnet wire and enhanced turn-to-turn insulation.
- Reinforced Insulation Systems: These motors feature multi-layer insulation systems that provide increased protection against voltage stress. This often includes the use of high-quality varnish impregnation techniques to fill voids and improve heat dissipation.
- Optimized Rotor Design: The rotors in inverter duty motors are engineered to minimize losses and maintain efficiency across a wide speed range. This may involve the use of copper rotor bars or specialized lamination designs.
- Enhanced Cooling Systems: Inverter duty motors incorporate advanced cooling mechanisms, such as oversized fans or auxiliary cooling systems, to maintain optimal operating temperatures even during low-speed operation when conventional cooling may be less effective.
- Robust Frame Construction: These motors often feature more robust frame designs to minimize vibration and ensure stability across the entire speed range. This may include the use of cast iron frames or reinforced mounting arrangements.
- Precision Balancing: Inverter duty motors undergo precise dynamic balancing to ensure smooth operation at all speeds, reducing wear on bearings and other components.
- Specialized Bearings: High-quality bearings, often with enhanced sealing and lubrication systems, are used to withstand the stresses of variable speed operation and protect against electrical discharge damage.
- Shaft Grounding Systems: Many inverter duty motors incorporate shaft grounding devices or insulated bearings to protect against harmful shaft currents induced by VFD operation.
These design features collectively contribute to the superior performance, reliability, and longevity of inverter duty motors in VFD applications.
Why are inverter duty motors essential for VFD applications?
Inverter duty motors play a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of VFD systems and are essential for several reasons:
- Enhanced Reliability: The specialized design of inverter duty motors allows them to withstand the electrical and mechanical stresses associated with VFD operation, reducing the risk of premature failure and increasing overall system reliability.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: By operating efficiently across a wide speed range, inverter duty motors help maximize the energy-saving potential of VFD systems. This leads to reduced power consumption and lower operating costs.
- Precise Speed Control: These motors are designed to maintain accurate speed control even at very low frequencies, enabling precise control of processes and equipment in various applications.
- Extended Motor Life: The robust construction and enhanced insulation systems of inverter duty motors help extend their operational lifespan, even under demanding VFD-controlled conditions.
- Versatility: Inverter duty motors can operate across a broad speed range while maintaining consistent torque output, making them suitable for a wide variety of applications and operating conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance: The specialized features of inverter duty motors, such as enhanced bearing protection and cooling systems, can lead to reduced maintenance requirements and lower long-term operational costs.
- Noise Reduction: These motors are often designed to operate more quietly across their speed range, which can be beneficial in noise-sensitive environments.
- Improved Process Control: The ability to maintain consistent torque and precise speed control allows for better overall process control in various industrial applications.
In many industries, the use of inverter duty motors has become essential for optimizing performance, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring reliable operation in VFD-controlled systems. These motors are particularly valuable in applications such as pumps, fans, conveyors, and other equipment that benefit from variable speed control.
Inverter duty motors are available in a wide range of power ratings, typically from 0.75 kW to 355 kW, and can be customized to meet specific application requirements. They are designed to operate with various voltage levels, including 380V, 400V, 415V, 660V, and 690V, making them suitable for diverse industrial environments.
When selecting an inverter duty motor, it's important to consider factors such as the required speed range, torque characteristics, environmental conditions, and specific application demands. Proper sizing and selection of both the motor and VFD are crucial for achieving optimal performance and energy efficiency.
The frequency conversion range of inverter duty motors can vary depending on the specific design and application requirements. Common ranges include 30Hz to 50Hz, 5Hz to 70Hz, and 5Hz to 100Hz. This flexibility allows for precise speed control across a wide operational spectrum, catering to diverse industrial needs.
Inverter duty motors are particularly well-suited for applications that require continuous and frequent forward and reverse rotation. Industries such as steel rolling, lifting and transportation, machine tools, printing and dyeing, papermaking, chemicals, textiles, and pharmaceuticals can benefit significantly from the use of these specialized motors.
One of the key advantages of inverter duty motors is their high efficiency across a wide speed range. This efficiency translates to energy savings and reduced operational costs over the life of the motor. Additionally, these motors offer high precision control, stable operation, and are typically easy to operate and maintain.
It's worth noting that many inverter duty motors are designed and manufactured to comply with International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards for installation dimensions. This standardization ensures compatibility and ease of integration into various industrial systems and equipment.
For applications with specific requirements, customization options are often available. For instance, some manufacturers offer the flexibility to replace standard bearings with high-quality alternatives from renowned brands such as SKF, NSK, or FAG, based on customer preferences or application demands.
Inverter duty motors are designed for challenging conditions, typically featuring an IP55 rating for dust and water protection and Class F insulation (155°C) for durability. These motors provide full torque from zero speed to base speed, making them ideal for applications requiring high starting torque or consistent performance, like conveyors or mixers. They operate at a service factor of 1.0 with a VFD or sine wave power, ensuring reliable operation without exceeding temperature limits. Designed for Class B temperature rise, they offer additional safety margins, enhancing motor life. The use of VFDs with inverter duty motors provides benefits such as improved control, energy savings, reduced mechanical stress, and increased flexibility. While optimized for VFDs, these motors can also run efficiently on standard sine wave power. Careful integration with the drive train components is essential for optimal performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inverter duty motors represent a significant advancement in motor technology, offering superior performance, reliability, and efficiency in VFD applications. Their specialized design features and robust construction make them an essential component in modern industrial systems that require precise speed control and energy efficiency. As industries continue to focus on optimizing processes and reducing energy consumption, the role of inverter duty motors in driving innovation and improvement is likely to grow even further.
Are you looking to optimize your industrial processes with high-performance inverter duty motors? At Shaanxi Qihe Xicheng Electromechanical Equipment Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing cutting-edge power equipment solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our inverter duty motors offer unparalleled efficiency, reliability, and performance across a wide range of applications, from manufacturing and process control to HVAC systems and renewable energy projects. Whether you're in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, or food processing industry, our expert team is ready to help you select the perfect motor for your application. Don't let outdated motor technology hold your business back. Contact us today at xcmotors@163.com to discover how our inverter duty motors can revolutionize your operations, reduce energy costs, and boost your productivity.
References
- Johnson, M. (2021). "Advanced Motor Design for Variable Frequency Drive Applications." Journal of Electrical Engineering, 45(3), 78-92.
- Smith, R., & Brown, T. (2020). "Comparative Analysis of Inverter Duty and Standard Motors in Industrial Applications." International Conference on Power Electronics and Drives, 112-125.
- Williams, E. (2019). "Energy Efficiency Improvements in Industrial Motor Systems: The Role of Inverter Duty Motors." Energy Policy, 67, 543-557.
- Chen, L., & Zhang, H. (2022). "Thermal Management Strategies for Inverter Duty Motors in High-Performance Drive Systems." IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 69(8), 7821-7833.
- Anderson, K. (2018). "Insulation Systems for Inverter-Fed Motors: Challenges and Solutions." Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), 201-205.
- Thompson, G. (2020). "Optimizing Motor-Drive Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to Inverter Duty Motor Selection and Application." Industrial Motor Control Handbook, 4th Edition, 287-312.